The beta cells located in the pancreas produce, store and release insulin. Their ultimate job is to respond to blood sugar spikes, but these cells function differently in people with diabetes. Learn more about beta cell decline and what it means to people with diabetes.
Located in the pancreas are beta cells that produce and secrete insulin. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the amount of glucose in the blood. Beta cells respond to raised blood glucose levels to regulate the amount of sugar in the blood. Beta cells work differently in people with diabetes. The immune system attacks and destroys them in people with type 1 diabetes. Beta cells are unable to produce enough insulin or the insulin produced is resistant to controlling blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes is a progressive disease and even if you do everything right in your medical plan, beta cells will stop producing insulin over time. When beta cells still produce insulin, the usual way to combat high blood sugars is to combat the insulin resistance. Besides the medication Metformin, the way to reduce insulin resistance is to lose weight and exercise daily. Because of eventual beta cell changes, it is important for people with diabetes to maintain regular medical checkups, test their blood sugar frequently and keep plenty of diabetes supplies on-hand for proper diabetes self-management.
- A new study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism revealed people with pre-diabetes may experience a faster decline in beta cell function. As a result, the disease in these patients may progress more quickly than expected. Proactive, quick treatment could be the answer. People who have impaired fasting glucose (FBS between 100-125) and impaired glucose tolerance should react swiftly to change poor lifestyle habits and lose weight. This means avoiding sugary, salty and fatty foods, as well as processed or fast foods with added preservatives. Losing just 10 pounds can help lower blood sugar and minimize the risks associated with diabetes. It is helpful to exercise for at least 150 minutes each week.
- Certain factors can affect beta cells and lead to their decline. There are some theories which include your immune system as well as glucose being toxic to the beta cells and causing them to die more quickly. Even genetics has been added to the reason why certain people lose beta cells more quickly than others. Other possible factors include being overweight or obese, stress, vitamin D deficiency and exposure to chemicals such as pesticide, phthalates and heavy metals. Talk to your doctor about taking vitamin D supplements. Try to spend 10 minutes in the sun each day without sunscreen. If you are overweight, discuss diet and exercise with your doctor before starting any type of program. Choose foods and personal care products that do not contain dangerous chemicals. Always read the labels before buying anything. Reduce stress by exercising, socializing and engaging in hobbies you enjoy. Tai chi, yoga and meditation can also relieve stress.
Beta cell function can decline which may cause blood sugar to rise. Understand that it may occur even when you do everything right. Your doctor will adjust your medications accordingly. Lifestyle changes can definitely go a long way too. Get enough sleep each day to lower your cortisol levels which raises blood sugars. Take all medications prescribed by your doctor as instructed. Eat right and do not forget your exercise program.
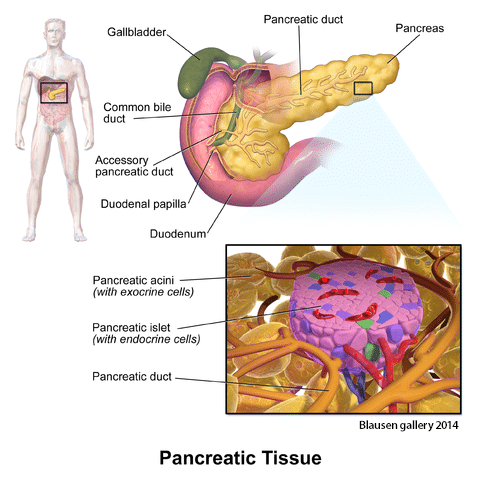 Located in the pancreas are beta cells that produce and secrete insulin. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the amount of glucose in the blood. Beta cells respond to raised blood glucose levels to regulate the amount of sugar in the blood. Beta cells work differently in people with diabetes. The immune system attacks and destroys them in people with type 1 diabetes. Beta cells are unable to produce enough insulin or the insulin produced is resistant to controlling blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes is a progressive disease and even if you do everything right in your medical plan, beta cells will stop producing insulin over time. When beta cells still produce insulin, the usual way to combat high blood sugars is to combat the insulin resistance. Besides the medication Metformin, the way to reduce insulin resistance is to lose weight and exercise daily. Because of eventual beta cell changes, it is important for people with diabetes to maintain regular medical checkups, test their blood sugar frequently and keep plenty of
Located in the pancreas are beta cells that produce and secrete insulin. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the amount of glucose in the blood. Beta cells respond to raised blood glucose levels to regulate the amount of sugar in the blood. Beta cells work differently in people with diabetes. The immune system attacks and destroys them in people with type 1 diabetes. Beta cells are unable to produce enough insulin or the insulin produced is resistant to controlling blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes is a progressive disease and even if you do everything right in your medical plan, beta cells will stop producing insulin over time. When beta cells still produce insulin, the usual way to combat high blood sugars is to combat the insulin resistance. Besides the medication Metformin, the way to reduce insulin resistance is to lose weight and exercise daily. Because of eventual beta cell changes, it is important for people with diabetes to maintain regular medical checkups, test their blood sugar frequently and keep plenty of 



Leave A Comment