People with diabetes may take several types of medications for different reasons. Each has specific instructions for use that affect your body. Discover the importance of knowing the names, instructions and doses for all medications prescribed.
- Typical medications often prescribed for people with diabetes include insulin, pills to lower blood sugar, blood pressure medication, aspirin, vitamin supplements, medication to lower cholesterol and others. Tell each doctor what medications and supplements you currently take to avoid contraindications. Discuss any allergies you have with your health care team. Share the names of all the doctors you visit to ensure they work together.
- Know the specific names, instructions and doses for each medication. Ask the doctor or pharmacist why the medication was recommended. Ask your diabetes educators to fit a predictable medication routine into your everyday schedule. Certain medications must be taken alone on an empty stomach while others need to be taken with food. Bring all labels or medications with you to medical appointments. Take notes or bring a family member to help you gather the information to properly take your medications. Keep a detailed list of your medications, including when they were prescribed and who prescribed them at home and in your wallet. Always carry a current list with you.
- Some medications are taken before you eat and others are taken afterwards. For example, metformin is used to help lower blood sugar and is typically taken with breakfast and with the evening meal. Often insulin injections are also taken before eating a meal. Knowing whether to eat or not is imperative to ensure diabetes medications work properly.
- Always take the exact prescribed dosage of medications. If there are any reactions, discuss them with your doctor immediately. Never change the dosage of any medication on your own. Certain medications must be taken at the same time daily, such as blood pressure medication.
- Many people with diabetes have vitamin deficiencies and should mention all symptoms to their health care team for assessment. Vitamin supplements should be taken with a glass of water. They can be taken on their own or with diabetes or high blood pressure medication. Ask the doctor what time of day is best to take required supplements. For example, it is usually better to take vitamin B early in the day for more energy.
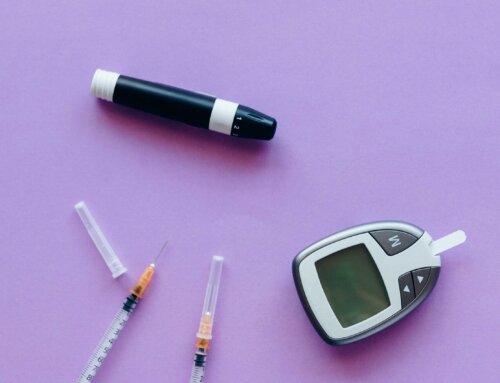
- Use a blood glucose monitor at home to check blood sugar levels and bring those records to every health care appointment. Have blood sugar A1C levels checked by a health care professional at least every three months. Find out the best times during the day to check your blood sugar levels. Have cholesterol levels checked at least yearly.
- When medicine is prescribed, inquire about the side effects. Always report adverse reactions to your doctor immediately. Let your doctors know about any supplements as well as medications. Verify the vitamins you take are suitable for people with diabetes and do not contain sugars or other ingredients that might make your blood sugar soar.
- Ask about how medications interact with the foods you eat. Proper diet and exercise remain an integral part of diabetes self-management when you take medication. Find out how medications and supplements might affect your blood glucose levels.
- If you forget to take a prescribed medication, ask a doctor or pharmacist about how to take the next dose. Some medications will be taken as soon as you remember. Others should not be taken off schedule and a dose might be missed. Always find out from a health care professional.
Maintain a list of all your diabetes medications that includes dosages and the time to take them as well as who prescribed them and when they were prescribed. Keep all medications out of the bathroom where humidity is present. It is essential to be well-organized and take your medicine as prescribed. Your health depends on it and mistakes can be potentially harmful.





Leave A Comment