What does it mean to be “pharmaceutical grade”?
There are three grades of fish oil: cod liver oil; health-food grade fish oil; and pharmaceutical-grade fish oil. Due to its inferior purification process, cod liver fish oil and food grade fish oils are found to contain some contaminants such as mercury, PCB’s, and DDT. Pharmaceutical-grade fish oils are molecularly distilled, using a highly complex purification process that removes all contaminants and preserves a much larger concentration of omega-3 fatty acids than the other forms of fish oils. In addition, pharmaceutical-grade omega-3 is the most neutral in taste and can be more easily digested than the other grades of fish oil. Diachieve Pharmaceutical-Grade Omega-3 is manufactured with the most stringent guidelines to ensure optimum purity and potency of EPA and DHA.
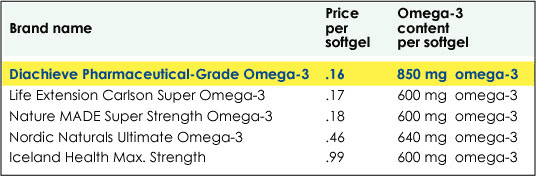
Cost per Gram
Diachieve’s pharmaceutical-grade fish oil contains a much higher content of omega-3 fatty acids per soft gel than many leading brands of fish oil. In fact, you might have to take two or three times the dosage just to get the same amount of omega-3 EPA and DHA that is in Diachieve Pharmaceutical-Grade Omega-3. To get the best value, you need to compare more than price when shopping for omega-3. Check supplements facts on the back of the label for omega-3 content per soft gel to determine how much you are paying per gram.
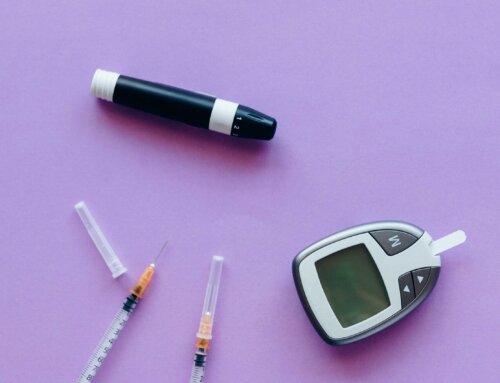
Omega3’s have been found to help improve diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a degenerative complication of diabetes. In a study publishedin the Journal of Neurochemistry on the protective effects of omega3 for diabetic neuropathy, it was found that fish oil had a a significant beneficial effect on nerve conduction velocity (NCV). (Ref: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.71020732.x/full)
- http://www.stopobesityalliance.org/steering-committee/steering-committee-members/american-diabetes-association/
- American Diabetes Association
- British Journal of Nutrition (published online ahead of print), doi:10.1017/S0007114509382173. Authors: M. Micallef, I. Munro, M. Phang, M. Garg
- Li, Jing-Jing; Chang J Huang, Dong Xie (2008-06). “Anti-obesity effects of conjugated linoleic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, and eicosapentaenoic acid”. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 52 (6): 631-645. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200700399. ISSN 1613-4133
- Weintraub, M S; R Zechner, A Brown, S Eisenberg, J L Breslow (1988-12). Dietary polyunsaturated fats of the W-6 and W-3 series Journal of Clinical Investigation 82 (6): 1884-1893. doi:10.1172/JCI113806. ISSN 0021-9738
- Woodman, Richard J; Trevor A Mori, Valerie Burke, Ian B Puddey, Gerald F Watts, Lawrence J Beilin (2002-11). “Effects of purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on glycemic control, blood pressure, and serum lipids in type 2 diabetic patients with treated hypertension”. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 76 (5): 1007-1015. ISSN 0002-9165




Leave A Comment