Formerly a disease that usually struck adults aged 40 and over, more health care providers are diagnosing children with type 2 diabetes. It is now one of the most common chronic diseases in children and teens. Find out more about children with type 2 diabetes including symptoms and healthy habits to ward off this disease.
- When a child gets diabetes, it is often assumed to be type 1 diabetes. Over the past two decades, more kids are facing type 2 diabetes. It can be hard to detect type 2 diabetes in children. Knowing the signs and symptoms helps parents get an earlier diagnosis to take action right away.
- Once called adult onset diabetes, type 2 diabetes now strikes people of all ages. Prevention and management are key issues to focus on with your children. Encourage kids to eat well-balanced portion controlled meals, maintain a healthy weight and get enough physical activity. Obesity and sedentary behavior increase the risk of getting type 2 diabetes along with family history.
- Certain children are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes including overweight or obese kids, children with at least one parent who has diabetes and certain ethnic groups such as Native American, Hispanic, Asian and African American. Sometimes there are no symptoms so ask your pediatrician about taking blood tests to check for diabetes. Your doctor may also refer you to an endocrinologist for other testing.
- Symptoms of type 2 diabetes in kids include frequent urination, fatigue, drinking lots of liquids and thick, dark skin by the elbows, knees, neck, groin, armpits and between fingers and toes. If you notice any of these symptoms, discuss them with your child’s doctor right away.
- Children with type 1 diabetes need insulin to maintain proper blood sugar levels because the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas. With type 2 diabetes the body produces insulin but does not respond to it normally, causing insulin resistance. Lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, losing weight and exercise can help kids with type 2 diabetes regulate their blood sugar levels. They may also be required to take oral diabetes medications.
- Kids should avoid salty or sugary snacks. Encourage your child to eat plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains and lean meats. There are also special sugar free foods for people with diabetes for those times when you child wants a treat.
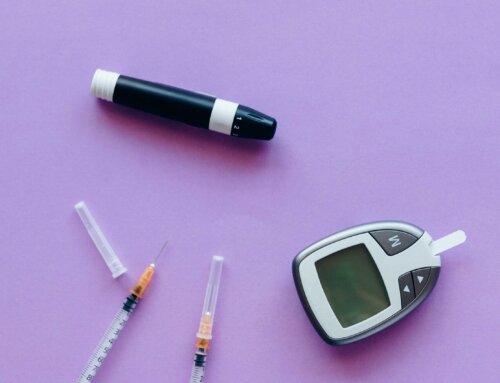
- Some kids and teens with type 2 diabetes need to take medicines, insulin shots or use insulin pumps. An insulin pump is about the size of a pager and delivers insulin in small doses right into the body. It eliminates the need to administer shots and can be worn discreetly. Certain parents and kids prefer this automatic method because it offers a more carefree lifestyle and more precise control.
- It is important to monitor the child’s blood sugar levels regularly according to the instructions given by a medical professional. Write down results each time the child’s blood sugar is checked and share them during physical exams.
- Typically children aged 11 and older can learn how to monitor their own blood sugar and be more proactive in self-management of diabetes. Younger children need help and support from parents and caregivers at school, camp and day care. Medical instructions should be given to people responsible for the child so they know how to handle everyday issues and emergency situations.
Type 2 diabetes in children can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, stroke and other health problems. There are professionals ready to help your child get the best possible treatment for a healthier life. Work with a health care team to ensure your child has a healthy body and positive attitude with type 2 diabetes.





Leave A Comment