People with type 1 diabetes depend on insulin to keep their blood sugar levels under control. Insulin is given in an injection or pump and can help prevent diabetes-related complications when used correctly.
Discover 3 important tips to keep in mind when taking insulin.
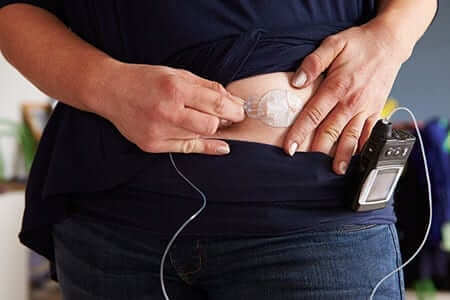
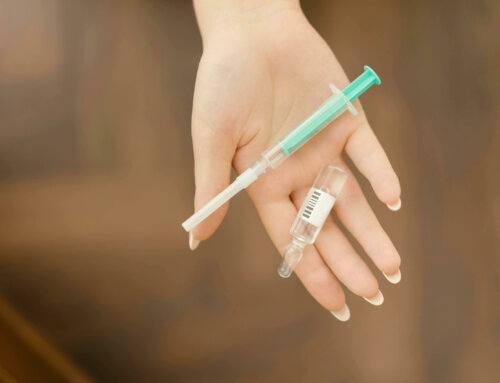
- People with diabetes may be concerned about giving themselves insulin shots which could be painful. The upper outer arms, abdomen and thighs have adequate amounts of fatty tissue which is preferred for insulin injections. Insulin injected in these areas is absorbed more quickly than using the hip and buttock areas. Using fatty areas minimizes the risk of injecting insulin too close to a nerve, muscle or large blood vessel. Inject the insulin about 4 inches above the knee and 4 inches down from the top of your leg on the outer side of the thigh. If you do not have much fat pinch up the fat to avoid hitting the muscle. Injecting insulin into a muscle will speed up its timing. Use the fatty tissue in the back of your arm located between the elbow and shoulder. If you inject it in your buttocks, stay away from the lower buttock area and use the wallet area near your hip also known as love handles. Avoid injecting insulin within two inches of your navel and stay away from your inner thigh area. Many people choose an insulin pen with pen needles because it is convenient, discreet and can be pre-measured. It is also good for someone with low vision since you can hear the click with each unit instead of drawing up the insulin. Take it easy on the force when you administer insulin with a pen. Hold the pen straight while you administer the insulin and use your thumb to depress the button. Keep it in place for 6 seconds after it is delivered to make sure no insulin leaks out. When using a bottle and syringe relax your muscles at the injection site and inject into your skin/fat quickly. If you use topical alcohol to clean the area make sure it is totally dry prior to injecting. This will reduce the burning sensation. Always verify there are no air bubbles in the syringe before using it; this could give you an injection with a reduced dose of insulin.
- Establish a routine for injecting insulin. Know the exact time of day you need to take insulin and give your injections in the same basic area. Make sure to switch injection sites within the same basic area. For example, you may choose to take your morning insulin in your thigh and your evening insulin in your arm. Be consistent to help your body better absorb the insulin. Try not to administer random injections. Having a regular pattern makes a big difference in your overall diabetes self-management plan. Massage or exercise after an injection can speed up the absorption of insulin due to increased circulation. If you plan to exercise after an injection, choose a spot that is not affected by the exercise. For example, do not inject insulin in you thigh if you plan to go running afterward.
- It is important to select a slightly new location on your body for each insulin injection. This is referred to as site rotation. Always take note of where your last injection was given. Move one or two inches to the side each time. Keep moving the injection site until you have covered all the available sites in that area then start a new area on your body. Make sure to maintain accurate records of your site injection. If you use the same area continually, fatty deposits may develop that make the skin appear lumpy and could delay the absorption of insulin. Stay away from scar tissue, varicose veins and broken blood vessels. Site rotation also helps to prevent skin irritations and infections. Make sure your supplies are fresh, in date and include new needles. Always store your insulin at the proper temperature. Avoid hot spots such as the glove compartment of your car or extreme cold areas such a freezer. Do not store insulin in the bathroom due to high humidity. It is most comfortable to use insulin at room-temperature. Use an insulated bag to store insulin on-the-go. Have a plan to properly dispose of needles and other insulin supplies when you are done. Always check your blood glucose levels throughout the day to determine the right amount of insulin to take. If you have blood sugar fluctuations or questions, contact your doctor right away.
Knowing the right way to administer insulin can help you maintain proper blood sugar levels and avoid potential complications. Using the right injection areas and site rotation makes a big difference. Talk to your diabetes health care team about the ideal schedule and administration sites when you take insulin.





Leave A Comment